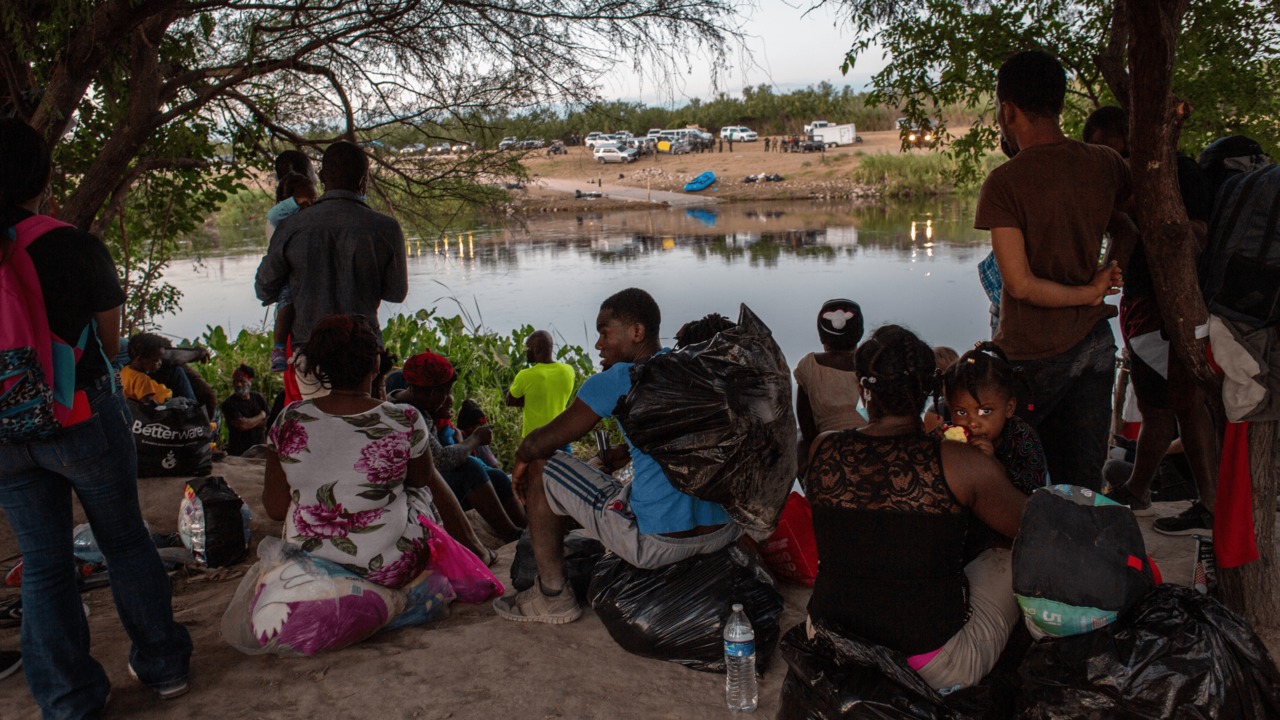
Many face expulsion because they are not covered by protections recently extended by the Biden administration to the more than 100,000 Haitian migrants already in the U.S., citing security concerns and social unrest in the Western Hemisphere’s poorest country. The devastating 2020 earthquake forced many of them from their homeland.
The United States and Mexico appeared eager to end the increasingly politicized humanitarian situation that prompted the resignation of the U.S. special envoy to Haiti and widespread outrage after images emerged of border agents maneuvering their horses to forcibly block and move migrants.
On Friday, President Joe Biden said the way the agents used their horses was “horrible” and that “people will pay” as a result. The agents have been assigned to administrative duties while the administration investigates.
“There will be consequences,” Biden told reporters. “It’s an embarrassment, but it’s beyond an embarrassment — it’s dangerous, it’s wrong, it sends the wrong message around the world and sends the wrong message at home. It’s simply not who we are.”
Meanwhile, Homeland Security has said that nearly 2,000 Haitians have been rapidly expelled on flights since Sunday under pandemic powers that deny people the chance to seek asylum. About 3,900 were being processed for a possible return to Haiti or placement in U.S. immigration court proceedings. Others have been released in the U.S. with notices to appear in court or to report to immigration authorities, and some returned to Mexico..
A U.S. official with direct knowledge of the situation said seven flights were scheduled to Haiti on Friday, six on Saturday and seven on Sunday. The official was not authorized to speak publicly.
And in Mexico, just over 100 migrants, most of them single men, remained Friday morning in the riverside camp in Ciudad Acuña.
Dozens of families who had been there crossed back to Del Rio overnight after Mexican authorities left the area. With the river running higher, some Border Patrol agents helped families who were struggling to cross with children.
Some migrants also moved to small hotels or private homes in Ciudad Acuña. Authorities detained six migrants at one on Thursday afternoon.
Luxon, a 31-year-old Haitian migrant who withheld his last name out of fear, said he was leaving with his wife and son for Mexicali, about 900 miles west along Mexico’s border with California.
“The option was to go to a place where there aren’t a lot of people and there request documents to be legal in Mexico,” he said.
Asked about the situation in Ciudad Acuña on Friday, Mexico President Andrés Manuel López Obrador said, “we don’t want Mexico to be a migrant camp, we want the problem to be addressed fully.”
At the Val Verde Border Humanitarian Coalition in Del Rio, migrants stepped off a white Border Patrol van on Friday, many smiling and looking relieved to have been released into the U.S. Some carried sleeping babies. A toddler walked behind her mother wrapped in a silver heat blanket.
A man who’d driven 200 miles from Ohio hoping to pick up a friend and her family wore a neon yellow vest and quietly scanned the line of Haitian migrants. Dave, who didn’t want to share his last name, didn’t see them in this group.
“I feel like my friend is worth my time to come down and help,” he said, explaining that he wore the vest so his friend — a nurse whom he’d met on a humanitarian trip to Haiti over a decade ago — would be able to spot him in the crowd when she arrived with her husband and 3-year-old daughter.
“I just see it as an opportunity to serve somebody,” said Dave, who considers himself a Trump supporter but hates how politicized the immigration issue has become. “We have so much.”
Some Haitians are being allowed to remain in the U.S. at least temporarily to seek asylum or to stay under some other claim to residency, with notices to appear later before immigration authorities. DHS officials declined to specify the number but said they are people with particular “vulnerabilities,” meaning they are pregnant, have young children or the U.S. doesn’t have the capacity to hold them in detention, especially during the pandemic.
The government has no plans to stop expelling others on public health grounds despite pressure from Democratic lawmakers, who say migrants are being sent back to a troubled country that some left more than a decade ago.
The Trump administration enacted the policy in March 2020 to justify restrictive immigration policies in an effort to prevent the spread of the coronavirus. The Biden administration has used it to justify the deportation of Haitian migrants.
A federal judge late last week ruled that the rule was improper and gave the government two weeks to halt it, but the Biden administration appealed.
Officials said the U.S. State Department is in talks with Brazil and Chile to allow some Haitians who previously resided there to return, but it’s complicated because some of them no longer have legal status there.
The Biden administration’s special envoy to Haiti, Daniel Foote, submitted a letter of resignation on Thursday protesting the “inhumane” large-scale expulsions of Haitian migrants.
Foote, who was appointed in July, wrote to Secretary of State Antony Blinken, saying he was stepping down immediately “with deep disappointment and apologies to those seeking crucial changes.”
“I will not be associated with the United States inhumane, counterproductive decision to deport thousands of Haitian refugees and illegal immigrants to Haiti, a country where American officials are confined to secure compounds because of the danger posed by armed gangs to daily life,” he wrote. “Our policy approach to Haiti remains deeply flawed, and my policy recommendations have been ignored and dismissed, when not edited to project a narrative different from my own.”
The career diplomat was known to be deeply frustrated with what he considered a lack of urgency in Washington and a glacial pace on efforts to improve conditions in Haiti.
State Department spokesman Ned Price disputed Foote’s assertions, saying his proposals had been “fully considered in a rigorous and transparent policy process.”
“Some of those proposals were determined to be harmful to our commitment to the promotion of democracy in Haiti and were rejected during the policy process. For him to say his proposals were ignored is simply false,” Price said.
The humanitarian group UNICEF also condemned the expulsions, saying Thursday that initial estimates show more than two out of three migrants expelled to Haiti are women and children, including newborns.
“Haiti is reeling from the triple tragedy of natural disasters, gang violence and the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Henrietta Fore, UNICEF’s executive director, who said those sent back without adequate protection “find themselves even more vulnerable to violence, poverty and displacement — factors that drove them to migrate in the first place.”
And Civil Rights leader Rev. Al Sharpton, who toured the camp on Thursday, said he’d witnessed “a real catastrophic and human disgrace” and vowed to “stand with our people and make sure asylum is treated in one way and one manner.”
Related posts:
Views: 0
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

















 September 25th, 2021
September 25th, 2021  Awake Goy
Awake Goy  Posted in
Posted in  Tags:
Tags: 
















